Alternative Therapies
Massage
Massage therapy provides several important health benefits, including improving blood circulation, relaxing muscles for an improved range of motion, and increasing endorphin levels (which helps improve mood and decrease the effect of chronic pain).

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is a very general term for a classification of therapies with similarities. Most cognitive-behavioral therapies have the following characteristics:
CBT is a collaborative effort between the therapist and the client. It is a highly instructive approach. Cognitive-behavioral therapists seek to learn what their clients want out of life (their goals) and then help their clients achieve those goals. The therapist’s role is to listen, teach, and encourage, while the client’s roles is to express concerns, learn, and implement that learning. A sound therapeutic relationship is necessary for effective therapy, but not the focus. CBT therapists believe that the clients change because they learn how to think differently and they act on that learning. CBT is based on the idea that our thoughts cause our feelings and behaviors, rather than external things, like people, situations, and events. Of various types of psychotherapy, Cognitive-behavioral therapy is considered among the most efficient and cost effective.

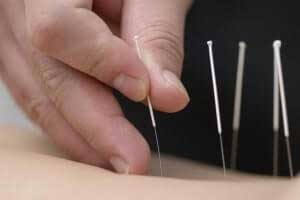
Acupuncture
Acupuncture has been claimed as an effective treatment for certain chronic pain. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) Consensus Development Conference Statement stated in November 1997 that acupuncture may be an effective adjunctive therapy for many pain conditions. Acupuncture has been claimed effective for various pain conditions including migraines, back pain, tennis elbow, menstrual cramps, fibromyalgia, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
Currently, much research has been done to search for the actual physiological effects acupuncture has on the body. Recent scientific research on acupuncture shows evidence of the neurochemical basis of acupuncture. It has been shown that specific frequencies of electrical stimulation of acupuncture points evoke the gene expression of specific neurohoromones. Clinical reports using this type of neuroelectric acupuncture have shown good results in treating health conditions such as various types of pain, depression, addiction, gastrointestinal disorders, and stroke (Ulett, J Han, & S Han, 1998).
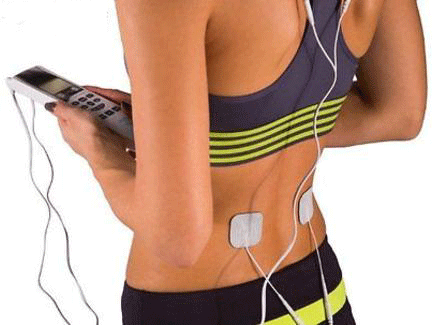
Physical Therapy for Pain Management
Physical therapy is an essential component of pain management. Pain is often the result of muscle, nerve or joint damage. The goal of physical therapy is to heal this damage, in order to eliminate the cause of the pain. Physical therapy also aims to improve function by working on strength, flexibility and range of motion in the affected body part. Physical therapy is very beneficial because it is individualized. Each patient is treated according to his or her needs. The focus of physical therapy varies from person to person depending on multiple factors such as site of injury and exercise tolerance.
Manual physical therapy is a commonly used therapy. It is a “hands on” approach that is often indicated for patients with headaches, spinal cord injuries, complex regional pain syndrome, neck and back pain and nerve or muscle injuries. These patients can get significant pain relief from this form of physical therapy, which does not use any special devices. Physical therapy is not limited to stretches, exercises and muscle manipulations. Various tools can be used to improve results. Examples of common devices include heated wax, ice packs, ultrasound, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS).
Physical therapy usually brings slow and steady relief from pain and discomfort. It is a non-invasive pain management option that is very safe. Some patients may initially experience mobility discomfort or pain, but these generally subside within a few days of starting physical therapy, improved flexibility, and strength.