Peripheral Neuropathy
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
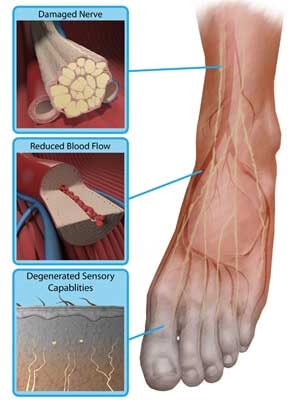
Peripheral neuropathy describes damage or disease affecting nerves which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health, depending on the type of nerve affected.
What are the types of Peripheral Neuropathy?
A number of types of peripheral neuropathy have been identified and classification is based on how many nerves and what type of nerves – motor, sensory, or autonomic – are damaged. Below are the common types:
-
- Mononeuropathy only affects a single nerve. The most common cause of mononeuropathy is a physical compression of the nerve. Carpal tunnel syndrome is an example of this. The “pins-and-needles” sensation is caused by the compression. Direct injury to a nerve, interruption of its blood supply, or inflammation can also cause mononeuropathy
- Mononeuritis multiplex, also known as polyneuritis multiplex involves damage to at least 2 or more nerves, typically in unrelated areas of the body. Mononeuritis multiplex can cause a loss of function of the muscle tissue that is innervated by the affected nerves. This is seen in conditions such as diabetes and typically presents as severe thigh pain followed by muscle weakness.
- Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy is damage or disease affecting multiple nerves and involving multiple parts of the body. A number of different disorders may cause polyneuropathy including diabetes and some vitamin deficiencies. In polyneuropathy, symptoms of burning, numbness and tingling are most severe in the feet.
- Autonomic neuropathy is a form of polyneuropathy that affects the non-voluntary, non-sensory nervous system, affecting mostly the internal organs such as the bladder muscles, heart, digestive system and genital organs.
- Neuritis is a general term for inflammation of a nerve, or the general inflammation of the peripheral nervous system. Symptoms depend on the nerves involved. Causes include physical injury, infection, chemical injury, radiation or underlying conditions and diseases.
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy causes are grouped as follows:
- Metabolic/endocrine: Diabetes Mellitus, chronic renal failure, liver failure, hypothyroidism
- Toxic causes: High alcohol intake, drugs, heavy metals, excessive intake of B6 (pyroxidine)
- Inflammatory diseases: Guillain-Barre syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, leprosy, multiple sclerosis, Lyme disease, sarcoidosis
- Adverse effects of Fluoroquinolones : irreversible neuropathy is a serious adverse reaction
- Others: HIV,AIDS, malignant disease, radiation, shingles
Diabetic neuropathy
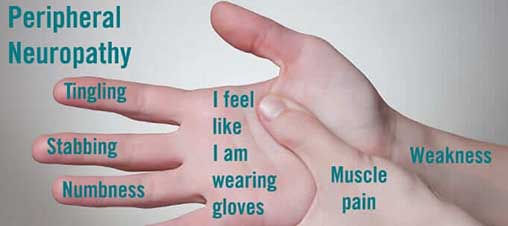
Peripheral neuropathy in diabetes is related to the sugar levels in the blood, and can sometimes be the first symptoms that present. Patients complain of burning sensation in their feet and pins and needles in their hands, known as ‘glove and stocking’ anaesthesia meaning the alteration in sensation is seen or the hands and feet. In addition, patients may have alteration in certain neurological signs such as the reflexes and muscle tone. Treatment of diabetic neuropathy primarily involves aggressive management of diabetes and good blood sugar control.
Alcoholic peripheral neuropathy
Individuals who consume large amounts of alcohol on a regular basis can develop peripheral neuropathy. The primary reason behind this is the loss of vital vitamins especially vitamin B6 and B12. These vitamins are responsible for the health of nerves and low levels can result in varying symptoms such as tingling, numbness and burning sensation in the hands and feet. The treatments are alcoholic peripheral neuropathy often involves complete abstinence from alcohol along with high-dose vitamins either administered as an intravenous drug or in the form of tablets.
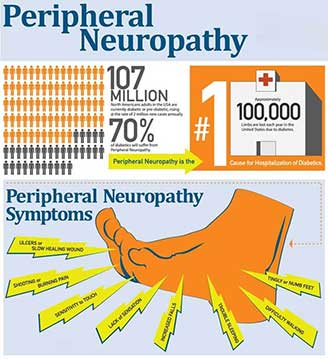
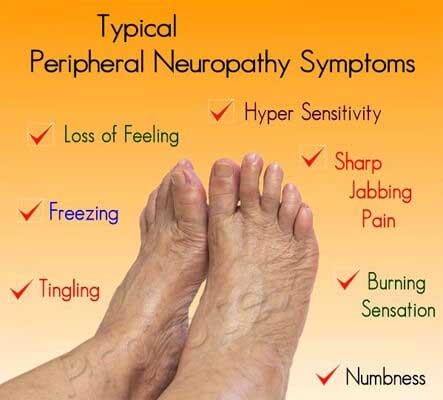
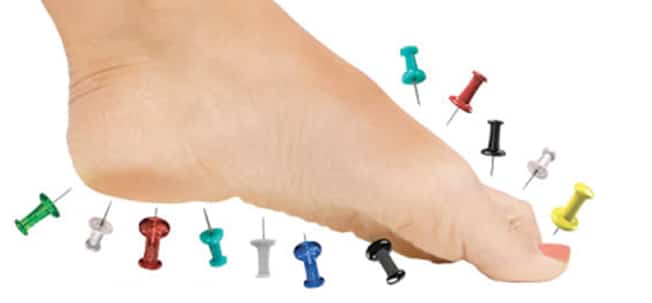
Signs and Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
Symptoms vary, depending on which types of nerves are affected. Common signs and symptoms may include gradual onset numbness and tingling in the feet or hands, burning pain, sharp, jabbing or electric-shock-type pain, extreme sensitivity to light touch. Individuals may experience muscle weakness or paralysis if motor nerves are affected, or heat intolerance and bowel/bladder or digestive problems if autonomic nerves are affected
Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is not a disease, but rather a symptom with many potential causes as described above. Diagnosis of underlying cause is obtained through a comprehensive medical history and examination. Certain tests that may be helpful include blood tests, imaging studies, nerve conduction studies. These will provide sufficient information to identify the cause of the peripheral neuropathy
In all the above cases, one main goal of treatment is to manage the condition causing the neuropathy. If the underlying cause is corrected, the neuropathy often improves on its own. Another goal of treatment is to effectively manage the painful symptoms. There are numerous powerful analgesics such as anticonvulsants medications and antidepressants that can be used in managing this condition. In addition, the use of lidocaine sprays and patches are useful as well. There is some evidence to support the use of opioids such as Morphine or Oxycodone, however their use can lead to dependence and addiction, so these drugs are generally only prescribed when other treatments fail.
The best way to prevent peripheral neuropathy is to carefully manage any medical conditions that may put you at risk.