Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
What is it?
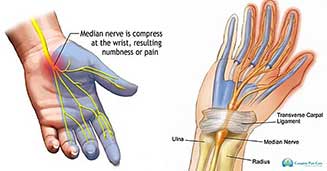
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a nerve pain condition of the hand. The wrist and base of the hand are made up of small bones called the carpals. Through these bones, tiny openings are present that allow the passage of blood vessels, ligaments, and nerves. In carpal tunnel syndrome, the opening that carries the main nerve for the hand, called the median nerve, is impinged. This entrapment can be caused by trauma and the misplacement of the carpals, but it is most commonly caused by the inflammation of a nearby ligament of the hand. When the median nerve is pinched, many symptoms can result. First, you can experience pain that extends into the hand. It is usually confined to the thumb, first two fingers, and the thumb side half of the ring finger. The small finger is generally not included in carpal tunnel syndrome. In addition to pain, you may experience tingling and numbness in these fingers, and some patients experience weakness. They are unable to use their hand and fingers for daily activities, such as typing or holding a steering wheel.
What kind of pain results?
Nerve pain is typically the sort of pain you can expect from carpal tunnel syndrome. Some patients can experience a cramping pain in their hand, but some also experience electric shock-like pains that shoot into their fingertips. Numbness can occur, and like the pain, it can occur in the thumb or the first three fingers. Symptoms may also appear in the thumb side half of the palm and wrist. You may additionally experience tingling in these regions of your hands or a pins and needles type of feeling. Weakness is commonly seen. In some cases, the weakness occurs when the causative task is performed, but it can also occur when other similar tasks or unrelated tasks are performed. Paralysis is rarely seen, but it is a possibility with any type of nerve pain, particularly if it is left untreated for a long period of time.
Who gets it?
Carpal tunnel can occur for a number of reasons. The most obvious reason is trauma to the hands that displaces the bones of the wrist. In this case, proper setting of the bones is necessary to ensure that the median nerve isn’t compressed. More common, however, it misuse and repetitive stress injuries of the hands. If you use improper form when typing or using the mouse, the ligaments in the hands can become inflamed. When they become inflamed from overuse, they can press on the median nerve and cause pain. It is important to use proper alignment when performing repetitive tasks. For instance, when typing, your hands should arch above the keyboard to keep the wrist in line with the fingers. Keyboard wrist guards are helpful in this situation to keep the wrist in alignment. Other activities can cause the hands to become awkwardly placed. Continuous driving, sports, and writing by hand can also stress the ligaments and cause carpal tunnel syndrome.
Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome requires a multidisciplinary approach. Many cases of carpal tunnel are treated conservatively, and this takes a few specialists to achieve. Occupational therapists are important adjuncts in helping with hand pain. They can teach you exercises to strengthen your hand muscles and increase your flexibility. They will help you to perform your daily tasks, with ergonomic considerations for your everyday tasks, can come up with alternative ways for you to complete the tasks. For instance, if buttoning a shirt causes pain, they can provide you with a tool that will assist you in buttoning your shirt.
Pain management specialists play an important role in controlling inflammation in the hand, finding the right balance of analgesics, and controlling the discomfort that usually arises from the condition. Steroid injections of the median nerve can decrease inflammation that be causing the impingement and relieve painful symptoms. Oral medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, anti-seizure drugs, and anti-depressants can also help reduce the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. A compounded cream with these medications as well as a local anesthetic agent may also help reduce symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome without the need to ingest the medications.
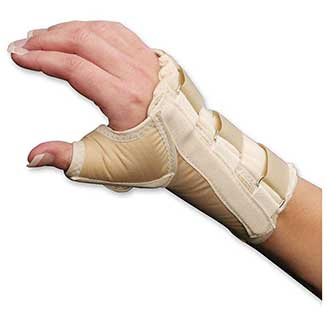
Finally, wrist braces can help, and they are worn at night or while performing task that require repetitive hand movements. If conservative management is not sufficient to help the pain, then it may be necessary to see a hand surgeon to correct the cause of the compression. An EMG/NC study is usually done before surgical intervention to confirm the diagnosis, determine what has caused the compression of the nerve, and outline steps to take to fix it.